Fruits are available at some positions on an infinite x-axis. You are given a 2D integer array
fruits where fruits[i] = [position<sub>i</sub>, amount<sub>i</sub>] depicts amount<sub>i</sub> fruits at the position position<sub>i</sub>. fruits is already sorted by position<sub>i</sub> in ascending order, and each position<sub>i</sub> is unique.You are also given an integer
startPos and an integer k. Initially, you are at the position startPos. From any position, you can either walk to the left or right. It takes one step to move one unit on the x-axis, and you can walk at most k steps in total. For every position you reach, you harvest all the fruits at that position, and the fruits will disappear from that position.Return the maximum total number of fruits you can harvest.
Example 1:
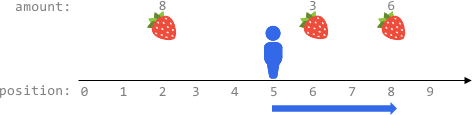
Input: fruits = [[2,8],[6,3],[8,6]], startPos = 5, k = 4
Output: 9
Explanation:
The optimal way is to:
- Move right to position 6 and harvest 3 fruits
- Move right to position 8 and harvest 6 fruits
You moved 3 steps and harvested 3 + 6 = 9 fruits in total.
Example 2:
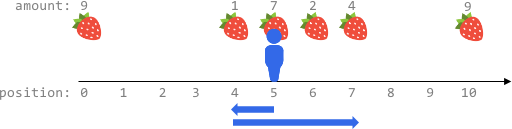
Input: fruits = [[0,9],[4,1],[5,7],[6,2],[7,4],[10,9]], startPos = 5, k = 4
Output: 14
Explanation:
You can move at most k = 4 steps, so you cannot reach position 0 nor 10.
The optimal way is to:
- Harvest the 7 fruits at the starting position 5
- Move left to position 4 and harvest 1 fruit
- Move right to position 6 and harvest 2 fruits
- Move right to position 7 and harvest 4 fruits
You moved 1 + 3 = 4 steps and harvested 7 + 1 + 2 + 4 = 14 fruits in total.
Example 3:
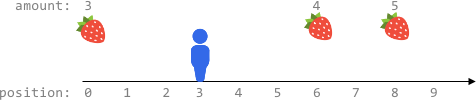
Input: fruits = [[0,3],[6,4],[8,5]], startPos = 3, k = 2
Output: 0
Explanation:
You can move at most k = 2 steps and cannot reach any position with fruits.
Constraints:
1 <= fruits.length <= 10<sup>5</sup>
fruits[i].length == 2`0 <= startPos, positioni <= 2 105
*positioni-1 < positionifor anyi > 0(**0-indexed**)
*1 <= amounti <= 104*0 <= k <= 2 * 105`题目大意:
向左向右在规定步数内采集每一格的水果,求最大水果数
算法思路:
一开始考虑用BFS,但由于每个点可以走两次,如先往左再往右,所以不能用BFS
每个点不能走3次,因为贪婪法。所以只要计算单向路径的水果数,单向路径水果数只要计算[startPos - k - 1, startPos + k + 1]的这个区间即可
然后重复路径的范围是[0, k/2 + 1], 枚举这些值然后用presum得到单向路径水果数。
注意事项:
- 先判断不合法的情况sum(gas) < sum(cost)
Python代码:
1 | def maxTotalFruits(self, fruits: List[List[int]], startPos: int, k: int) -> int: |
算法分析:
时间复杂度为O(k + n),空间复杂度O(n + k)



