Given a
file and assume that you can only read the file using a given method read4, implement a method read to read n characters. Your method read may be called multiple times.Method read4:
The API
read4 reads four consecutive characters from file, then writes those characters into the buffer array buf4.The return value is the number of actual characters read.
Note that
read4() has its own file pointer, much like FILE *fp in C.Definition of read4:
Parameter: char[] buf4
Returns: int
buf4[] is a destination, not a source. The results from read4 will be copied to buf4[].
Below is a high-level example of how
read4 works: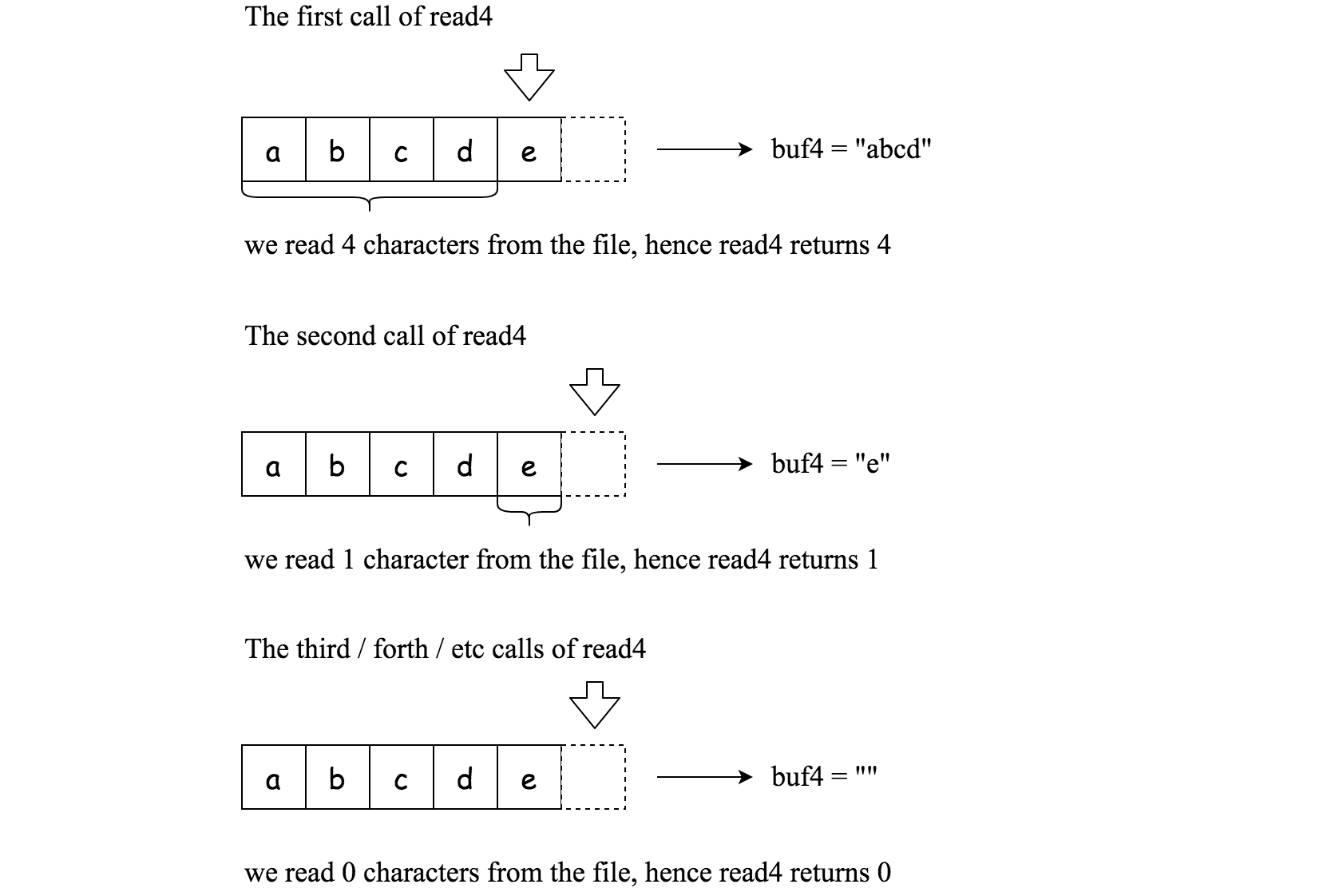
File file(“abcde"); // File is "abcde", initially file pointer (fp) points to 'a' char[] buf4 = new char[4]; // Create buffer with enough space to store characters read4(buf4); // read4 returns 4\. Now buf4 = "abcd", fp points to 'e' read4(buf4); // read4 returns 1\. Now buf4 = "e", fp points to end of file read4(buf4); // read4 returns 0\. Now buf4 = "", fp points to end of file
Method read:
By using the
read4 method, implement the method read that reads n characters from file and store it in the buffer array buf. Consider that you cannot manipulate file directly.The return value is the number of actual characters read.
Definition of read:
Parameters: char[] buf, int n
Returns: int
buf[] is a destination, not a source. You will need to write the results to buf[].
Note:
Consider that you cannot manipulate the file directly. The file is only accessible for
read4 but not for read.
The read function may be called multiple times.Please remember to RESET your class variables declared in Solution, as static/class variables are persisted across multiple test cases. Please see here for more details. You may assume the destination buffer array,
buf, is guaranteed to have enough space for storing n characters.It is guaranteed that in a given test case the same buffer
buf is called by read.Example 1:
Input: file = “abc”, queries = [1,2,1]
Output: [1,2,0]
Explanation: The test case represents the following scenario:
File file(“abc”);
Solution sol;
sol.read(buf, 1); // After calling your read method, buf should contain “a”. We read a total of 1 character from the file, so return 1.
sol.read(buf, 2); // Now buf should contain “bc”. We read a total of 2 characters from the file, so return 2.
sol.read(buf, 1); // We have reached the end of file, no more characters can be read. So return 0.
Assume buf is allocated and guaranteed to have enough space for storing all characters from the file.
Example 2:
Input: file = “abc”, queries = [4,1]
Output: [3,0]
Explanation: The test case represents the following scenario:
File file(“abc”);
Solution sol;
sol.read(buf, 4); // After calling your read method, buf should contain “abc”. We read a total of 3 characters from the file, so return 3.
sol.read(buf, 1); // We have reached the end of file, no more characters can be read. So return 0.
Constraints:
1 <= file.length <= 500file consist of English letters and digits.
1 <= queries.length <= 10*
1 <= queries[i] <= 500题目大意:
题意类似于LeetCode 157 Read N Characters Given Read4,但此题唯一的区别是这个新的API: def read(self, buf, n)会被调用多次
解题思路:
因为read调用多次,所以调用read4多读了几个字符在n以外的,需要保留下来让下一次read返回到结果中,所以用queue来保存中间结果
解题步骤:
N/A
注意事项:
- 先将read4的结果保存在self.queue中,然后再填充到buf中,这里用到了quicksort里面partition的方法,while中只有当填充buf时i才移动,而read4时候不移动
Python代码:
1 | def __init__(self): |
算法分析:
时间复杂度为O(n),空间复杂度O(1)



