Given the 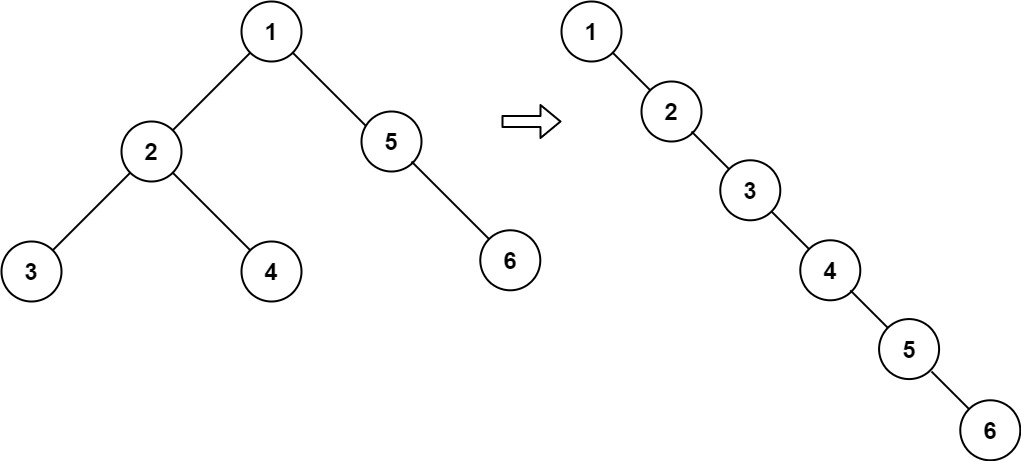
Example 2:
Example 3:
Constraints: The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
root of a binary tree, flatten the tree into a “linked list”: The “linked list” should use the same TreeNode class where the right child pointer points to the next node in the list and the left child pointer is always null. The “linked list” should be in the same order as a pre-order traversal of the binary tree. Example 1: 
Input: root = [1,2,5,3,4,null,6]
Output: [1,null,2,null,3,null,4,null,5,null,6]
Example 2:
Input: root = []
Output: []
Example 3:
Input: root = [0]
Output: [0]
Constraints: The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 2000]. -100 <= Node.val <= 100 Follow up: Can you flatten the tree in-place (with O(1) extra space)?题目大意:
将二叉树转成以右节点相连的LL
解题思路:
递归需要知道左右递归末尾节点,这样才可以将右节点的首节点接到左节点的末尾。所以递归函数输入是root,返回LL末尾节点
解题步骤:
N/A
注意事项:
- 递归函数输入是root,返回LL末尾节点
- 如果left_end是空,也就是没有左节点,就不用交换。返回right_end, left_end, root三者中非空者。
Python代码:
1 | def flatten(self, root: TreeNode) -> None: |
算法分析:
时间复杂度为O(n),空间复杂度O(1)



