Given a reference of a node in a connected#Connected_graph) undirected graph.
Return a deep copy (clone) of the graph.
Each node in the graph contains a val (int) and a list (List[Node]) of its neighbors.
class Node {
public int val;
public List neighbors;
}
Test case format:
For simplicity sake, each node’s value is the same as the node’s index (1-indexed). For example, the first node with val = 1, the second node with val = 2, and so on. The graph is represented in the test case using an adjacency list.
Adjacency list is a collection of unordered lists used to represent a finite graph. Each list describes the set of neighbors of a node in the graph.
The given node will always be the first node with val = 1. You must return the copy of the given node as a reference to the cloned graph.
Example 1:
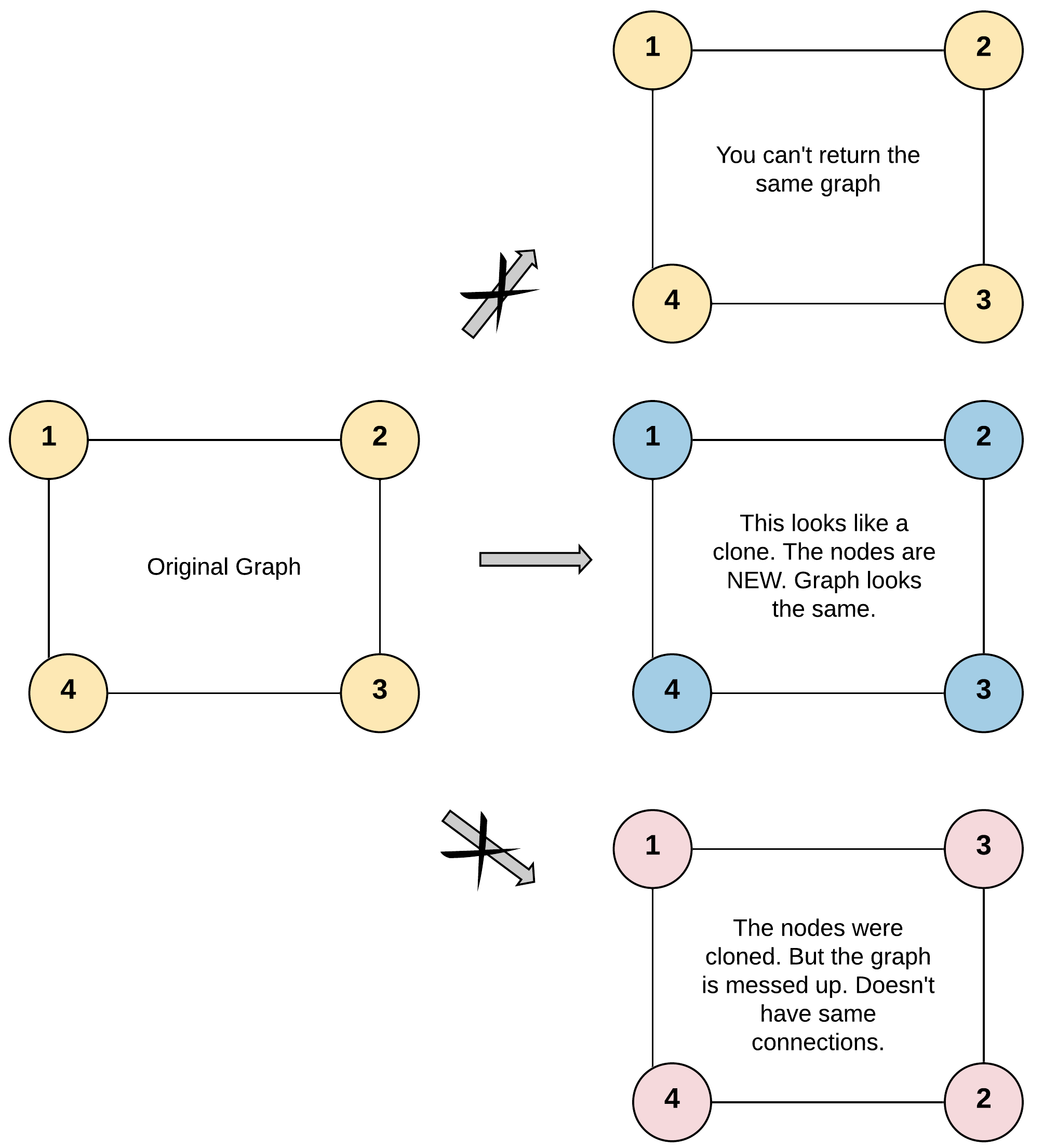
**Input:** adjList = [[2,4],[1,3],[2,4],[1,3]] **Output:** [[2,4],[1,3],[2,4],[1,3]] **Explanation:** There are 4 nodes in the graph. 1st node (val = 1)'s neighbors are 2nd node (val = 2) and 4th node (val = 4). 2nd node (val = 2)'s neighbors are 1st node (val = 1) and 3rd node (val = 3). 3rd node (val = 3)'s neighbors are 2nd node (val = 2) and 4th node (val = 4). 4th node (val = 4)'s neighbors are 1st node (val = 1) and 3rd node (val = 3).
Example 2:
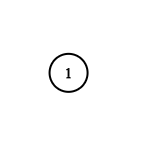
**Input:** adjList = [[]] **Output:** [[]] **Explanation:** Note that the input contains one empty list. The graph consists of only one node with val = 1 and it does not have any neighbors.
Example 3:
**Input:** adjList = [] **Output:** [] **Explanation:** This an empty graph, it does not have any nodes.
Example 4:
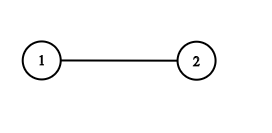
**Input:** adjList = [[2],[1]] **Output:** [[2],[1]]
Constraints:
1 <= Node.val <= 100Node.valis unique for each node.- Number of Nodes will not exceed 100.
- There is no repeated edges and no self-loops in the graph.
- The Graph is connected and all nodes can be visited starting from the given node.
题目大意:
深度复制图。注意要复制所有邻接节点。
算法I解题思路(推荐):
三步走。分开写逻辑会显得清晰点。
- BFS搜索所有节点,变成
邻接表节点列表。 - 复制节点。旧新节点映射存在dict中
- 根据node.neighbors复制边。
注意事项:
- 空节点判断Line 2-3
- BFS访问是收集节点列表,并不是变成邻接表。如果是含循环的图,由于用了visited,所以邻接表只能复制一半的边,不能用邻接表
Python代码:
1 | def cloneGraph(self, node: 'Node') -> 'Node': |
Java代码:
1 | // another bfs3 method uses 3 steps, convert graph to adjacent list by bfs (flatten the graph), |
算法II解题思路:
不分开三步写
Java代码:
1 | public UndirectedGraphNode cloneGraph2(UndirectedGraphNode node) { |
算法II解题思路:
DFS。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19public UndirectedGraphNode cloneGraph(UndirectedGraphNode node) {
HashMap<Integer, UndirectedGraphNode> map = new HashMap<Integer, UndirectedGraphNode>();
return cloneGraphR(node, map);
}
public UndirectedGraphNode cloneGraphR(UndirectedGraphNode node,
HashMap<Integer, UndirectedGraphNode> map) {
if (node == null)
return node;
if (map.containsKey(node.label))
return map.get(node.label);
UndirectedGraphNode result = new UndirectedGraphNode(node.label);
map.put(node.label, result);
for (UndirectedGraphNode child : node.neighbors) {
result.neighbors.add(cloneGraphR(child, map));
}
return result;
}
算法分析:
时间复杂度为O(# of results),空间复杂度O(lengh(high))。



